EVS
Computer
English
Hindi
G.K
Maths
Syllabus
Next Class will be upload of Online Exam
Question 1:
शेर किसान से क्या लेने गया था?
Answer:
शेर किसान से उसका बैल लेने गया था।
Question 2:
शेर ने बित्तो को राक्षसी क्यों समझ लिया?
Answer:
बित्तो ने एक चाल चली उसने किसान से कहा कि तुमने तो चार शेर फाँस रखे थे, यहाँ तो एक ही है। चलो कोई बात नहीं एक ही शेर नाश्ते के लिए काफ़ी है। यह सुनकर शेर ने बित्तो को राक्षसी समझ लिया। बित्तो का पहनावा भी ऐसा था। उसने सिर पर पग्गड़ और हाथ में दराँती पकड़ रखी थी, जिसे देखकर शेर डर गया।
Question 3:
बैल की जान कैसे बच गई?
Answer:
बैल की जान बित्तो की समझदारी व चतुराई से बच गई। उसने चार शेरों के नाश्ते की बात कही, तो शेर अपनी जान बचाकर भाग गया और बैल बच गया।
Question 1:
नीचे कुछ शब्दों के नीचे रेखा खिंची हुई है। उन्हें ध्यान में रखते हुए नीचे लिखे वाक्यों को अपने शब्दों में लिखो।
(क) बित्तो घोड़े पर सवार हो गई।
(ख) तुम घर की गाय को शेर के हवाले कर रहे थे।
(ग) आज एक राक्षसी से पाला पड़ गया।
(घ) अगर बैल आपके हाथ न आए तो मेरा नाम भेड़िया नहीं।
(ङ) शेर को देखते ही किसान के होश-हवास गुम हो गए।
Answer:
(क) घोड़े पर बित्तो सवार हो गई।
(ख) घर की गाय को ही तुम शेर के हवाले कर रहे थे।
(ग) एक राक्षसी से आज पाला पड़ गया।
(घ) आपके हाथ बैल न आए तो मेरा नाम भेड़िया नहीं।
(ङ) जैसे ही किसान ने शेर को देखा उसके होश हवास गुम हो गए।
Question 1:
शेर तो डर कर भाग गया। सोचो तो भेड़िए का क्या हुआ होगा?
Answer:
शेर की पूँछ भेड़िए की पूँछ से बंधी थी। जब शेर डर कर भागा होगा, तो उसके साथ ही भेड़िया भी घसीटता गया होगा। इससे भेड़िया बहुत घायल हो गया होगा। उससे चोटें आई होगीं, उसकी कई हड्डियाँ टूट गई होगीं।
Question 2:
शेर किसान के पास कितनी बार गया था? कहानी देखे बिना बताओ।
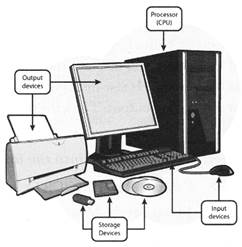
Input and Output Devices
Introduction
The computer will be of no use unless it is able to communicate with the outside world. Input/output devices are required for users to communicate with the computer. An input device send information to a computer system for processing. An input device tor a computer allows you to enter information. An output device can receive data from another device, but it cannot send data to another device. There are different devices of he computer that help it to do work.
Input Devices
The devices which are used to input the data and the program in the computer are known as “Input Devices”. For the text input, keyboard are used, microphone is used for audio or sound input.

Keyboard
The keyboard is the most common input device. A ‘keyboard’ is a human interface device which is “-presented as a layout of buttons. It is a text based input device that allows the user to interact with the computer through a set of keys mounted on a board.

Mouse
After the keyboard, the mouse is the most common type of input device. A mouse makes the process of navigating the screen much easier than trying to use just a keyboard. A mouse usually uses a ball, light or a laser to track movement.

Joystick
A joystick is an input device consisting of a large pointed stick and input buttons on it. We can use this for playing games on the computer. The joystick is a vertical stick which moves the graphic cursor in a direction the stick is moved. It typically has a button on top that is used to select the option pointed by the cursor.

Optical Mark Reader (OMR)
An OMR is a device which detects alpha numeric characters printed or written on a paper.
Magnetic Ink Character Reader (MICR)
The MICR is an input device or a technology used to verify the original paper documents, especially cheques.
Bar Code Reader
A bar code Reader also called a price scanner of point-of-scale (POS) Scanner, is a hand held or stationary input device, used to read information contained in a bar code.
Output Devices
An output device is used to send data from a computer to another device used. They are pieces of hardware that process data sent from a computer and translate it into a form readable by human. This information can be inany form that includes text, sound, images, etc. Output devices such as a printer, video display or speaker present data from a computer to a user. Thus we see that output devices are things we use to get information of a computer that has been held o generated within a computer.

Monitor
The Monitor is an output device that resembles with television screen and uses a CRT (Cathode Ray Tube) and LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) to display information. It is associated with a keyboard for manual input of characters and displays the information as it is keyed in. It also displays the program or application output. 1 hus, the monitor displays the results ot the computer s activities von the screen.

Monitor are classified into the following types:
v Cathode Ray Tube (CRT)
v Monochrome Monitor
v LCD or Flat Monitor
Printer
Printers are output devices used to produce paper (commonly known as hardcopy) output of documents stored in an electronic form. Based on the technology used, they can be classified as Impact and Non-impact printers.

Types of impact printer are:
v Dot Matrix Printer
v Daisy Wheel Printer
v Line Printer
v Drum Printer
v Chain Printer
v Band Printer
Speaker
Speaker is one of the most common output device. It is a device that converts analog audio signals into the equivalent air vibrations in order to make audible sound. They receive audio input from the computer’s sound card and produce audio output in the form of sound waves.

Input / Output Devices
In computing input/output or I/O refers to the communication between an information processing system (such as a computer) and the outside world. With the help of a dual purpose device, we can enter data into the computer as well as we can output data from the computer. Good examples of an input/output device are a CD-ROM and DVD-ROM units and a hard disk drive.
USB Flash Drive
USE Flash drive or thumb drive or pen drive is used when it is connected in the USB slot of the CPU Cabinet. These type of devices is used for data storage. USB Flash drive is available with different capacities.

CD-ROM
You must have seen or used CDs for watching movies, playing games and listening to music. CD-ROM is an acronym of “Compact Disc Read-Only Memory”. It is a type of optical disk capable of storing large amounts of data ? up to 1GB, although the most common size is 700MB (Megabytes).

Touch Sensitive Monitor
From the ancient period, human beings have been exploring and manipulating objects with their hands to sense the size, shape, texture and mass, etc. A Touch Sensitive Monitor is a pointing device that enables the user to interact with the computer by touching the screen. A touch screen is an electronic visual output that can detect the presence and location of a touch within the display area.

Adjective and Adverb
Adjectives:
An adjective is a word that describes other words.
Look at the following examples.
1. My house is very beautiful.
2. This is an antique vase.
3. This colour is so bright.
4. You have grown so tall.
5. The film looks interesting.
Adverbs:
An adverb is a word that describes a verb, an adjective or another adverb.
Look at the following examples.
1. He runs quickly.
2. She walks slowly.
3. She is very pretty.
4. He behaved very badly
5. I have read many books.
A Good House and Surroundings
- A good house should be clean and airy with windows and ventilators. Sunlight and fresh air keep the rooms dry and free from germs. A good house should have separate place for eating, sleeping, studying, cooking, washing and storage.
- A good house should have an open space for sitting out and for the children to play. It should have bolts on the doors and windows and locks on the cupboards.
- A good house should have proper drains to take away dirty water from the kitchen and bathrooms. It should have proper chimneys to let the smoke out.
- To keep our houses clean, we should keep our surroundings also clean. If our surroundings have garbage, they attract flies and germs which cause diseases.
- We should not throw our garbage around and make the surroundings dirty. The household garbage should be kept in closed dustbins. These dustbins should be taken to municipal bins or garbage dumps. Municipal trucks will carry this garbage away from the city.
- We should not let waste water to flow into open space and stagnate it near the houses. Mosquitoes breed in stagnated water and cause malaria. We should dispose waste water through drains. We should spray kerosene on stagnated water to kill mosquitoes.
Time
Clocks:
- A clock has two hands : (i) long hand and (ii) short hand
- The long hand is called minute hand and the short hand is called hour hand.
- Some clocks have a third hand called second hand. It moves much faster than the other two hands
- The dial of the clock is divided into 12 equal divisions marked as 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11 and 12
- 1 hour = 60 minutes I minute = 60 seconds
- ∴1 hour = 60 × 60 = 3600 seconds
- The hour hand takes 12 hours to complete one round.
- The minute hand takes 1 hour to complete one round.
Some conversions:
- 1 day = 24 hours; 1 week = 7 days; 1 month = 4 weeks; 1 year = 12 months 1 year = 52 weeks; 1 year = 365 days
- The time from 12 midnight to 12 noon is noted as A.M. (Anti Meridian) and the time form
12 noon to 12 midnight as P.M. 4Post Meridian).
How Data is Stored in Computer
Introduction
It would be inconvenient to study, work, cook, sleep, eat and relax, all in the one room of your house. It will be very difficult for you to trace the things which you want and work peacefully. However, a house is divided into different rooms such as the living room, dining room and study room, etc. with each room containing the required things so that it is comfortable for you to live there. In the same way computer uses its memory for storage information. The storage of a computer is divided into many parts that are called partioning of the storage. In the case of RAM, the particular memory location contains the information. The main storage of a computer is partitioned and formatted for making the smallest logical area that are called sectors.
What is a File?
Computer files are the blocks for storage information. Imagine that you have only one notebook for doing homework and class work for all subjects. If you wish to study English notes, you will have to check the whole notebook page-by-page to find what you need. But if you make separate notebooks for class work and homework and separate notebooks for different subjects this job will become very easy. A file may contain text, image, sound, video information. Whereas, a folder- contains many files and another folders. If we consider the notebook is a folder then the English notes is a file and heading of English note may considered as the name of that file.
We know that the application software is used for performing the specific task, such as, MS Word is mainly used for editing text, Ms Excel is mainly used for editing numerical based work and Ms Powerpoint is mainly used for presentation of images. Each of the work done in the application is saved with the type of file in which work has one. For example: Word file is saved with .docx extension with name of that file. Excel file is saved with .xlsx extension along with name of that file and powerpoint file is saved with .pptx extension along with name of that file. Every file can be identified by its extension code to show from which type of application it belongs to.
Files on a computer can be created, moved, modified and deleted. We cannot get back or restore a file, once we delete it from the Recycle Bin.
In other words, a File is the actual space taken by the data on the disk. Information in a computer file can consist of smaller packets of information (often called ‘records’ or ‘lines’). When you save any work done on the computer, it occupies some memory of the computer.
In Windows, a file is symbolized by the following icon:
What is Directory?
Directories are like the drawers of an office table. Files are like the actual things that we keep in the drawers. A directory is also known as a folder. A directory is a location for storing files on your computer. For example, files containing drawings can be put into the Drawing folder, files containing text can be put into the Text folder. Different types of folders are made so that various types of files can be stored in them in an organized manner. We can create folders within a folder. These are called sub-folders. Therefore, a directory allows you to group your files in a meaningful way.

A directory is a logical area on the hard disk or storage where files are kept. Each directory is used to keep one type of file.
Data Measurement System
Suppose you are asked where you live or the name of your friends, you will reply immediately because you remember them and this information is already in your memory. A computer also has a memory which stores a lot of information inside it. A computer stores everything in its storage.
The unit of data measurement is a bit, which can store a value (one) or no-value (zero) thus having a binary nature.
Bit is the smallest measuring unit of computer memory. It means binary digits. Just like we use kilograms and grams to measure weight, the computer’s memory is organized as a collection of bytes.
A byte is the basic unit that is used to represent the alphabetic, numeric and alphanumeric data. Byte is a unit of measurement of computer memory. Each number, alphabet or special character takes place of one byte. For example, the name Zacob needs 5 bytes for its storage.
Large amounts of memory are indicated in terms of kilobytes (1,024 bytes), megabytes (1,048,576 bytes), gigabytes (1,073,741,824 bytes) and terabytes (1099511627776 & bytes.)
Units to measure memory are given in the following table:
Bit = 0 or 1
Nibble = 4 Bits
1 Byte (b) = 8 Bits
1 Kilobyte (KB) = 1024 B
1 Megabyte (MB) = 1024 KB
1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1024 MB
1 Terabyte (TB) = 1024 GB.
Synonyms and Antonyms
Synonyms: Words having similar meaning.
| Word | Synonyms |
| Aid | Help, relief, support |
| Brave | Courageous, intrepid, impudent |
| Clever | Able, skillful, intelligent |
| Courage | Boldness, valour, bravery |
| Deliver | Relieve, rescue, discharge |
| Destroy | Demolish, ruin, raze |
| Dull | Stupid, blunt, boring |
| Ecstasy | Joy, bliss, enthusiasm |
| Gift. | Present, donation, contribution |
| Ideal | Model, perfect, example |
| Junk | Rubbish, waste, refuse |
Antonyms: Word having opposite meaning.
| Word | Antonyms | Word | Antonyms |
| Agree | Disagree | Alone | Together |
| Arrive | Depart | Big | Small |
| Brave | Coward | Before | After |
| Belief | Disbelief | Cool | Hot |
| Cruel | Kind | Clean | Dirty |
| Dry | Wet | Dull | Interesting |
| Evil | Good | Few | Many |
| Foolish | Wise | Follow | Lead |
| Famous | Ordinary | Forget | Remember |
| Faithful | Unfaithful | Fat | Thin |
| Fair | Unfair | Far | Near |
| Fresh | Stale | Gain | Loss |
Our Clothes
- Long long ago people wore animal skins for clothes. Today we wear clothes made of cotton, silk, wool, nylon. Clothes are of different types and made in different ways.
- The cotton plants have fruits or cotton bolls which burst open. The fluffy cotton inside these bolls is picked out. It has thin threads or fibres in it. They are twisted together or spun to make long threads.
- These cotton threads are woven together to make cloth. The weaving of the threads is done on a machine called loom. The people who weave clothes are called weavers. After weaving, the cloth may be colored or dyed.
- Silk clothes are made from saliva of an insect called silkworm. When the silkworm is in pupa stage it secretes saliva and builds cocoon around itself. These pupae are heated in boiling water and the worms inside are killed.
- Silk thread is obtained from the pupae. Then the threads are dyed and cloth is prepared.
- Woollen clothes are made in a General science the wool of sheep. Woolen clothes keep us warm.
- Naphthalene balls and dried leaves of neem keep insects away from the clothes.
- Nylon and terylene are synthetic fibres prepared from carbon compounds.
Measurement
- Non-standard Units of Length:
- Length → fingers, hand span, cubit, pace etc.
- Standard Units of Length:
- Meter is a standard unit for measuring length.
- 1 meter = 10 decimetres
- 1 decimeter = 10 centimetres
- 1 metre = 100 centimetres
- Non-standard Units for Mass:
- Mass → marbles, stones, beads etc.
- Standard Units for Mass:
- Kilogram is a standard unit of mass.
- 1 kilogram = 1000 grams
- Non – Standard Units of Capacity:
- Capacity → Cup, bottle, tumbler etc.
- Standard Units of Capacity:
- Liter is a standard unit of capacity.
1 liter = 1000 milliliters
Better Ways of Using Computer
Introduction
Sitting in front of computer for long time such as, 7 to 8 hours in a day may worse impact on your health later. The use of computers for long hours is a major issue of computer-related health risks which include repetitive stress injuries, eyestrain, obesity, back problems, etc. As for any task that means working in one position for sometime, it’s important to make yourself as comfortable as possible when you use your computer. Correct postures pay off in later life and will help to minimize potential problems. In this chapter, we study about the correct posture while sitting in front of computer.
Correct Postures While Using Computers
Weather you are using windows PC, Laptop, it is important to maintain proper body posture while using these devices. Sitting at a computer for long periods of time can take a toll on your body. By not sitting with the correct posture, it is easy to end up with back pain, neck pain, knee pains and a tingling of the hands and fingers. Correct postures play a large role hence we should follow the good habits. When we use the computer.
Do’s and Don’ts
Some of the computer’s Do’s and Don?ts are the following:
(1) You should Adjust your chair height so your feet are flat on the floor and your knees are in line with your hips.
(2) You should sit up straight in front of computer.
(3) Ensure the keyboard is close and directly in front of you.
(4) To help your neck stay relaxed and in a neutral position, the monitor should be directly in front of you, a few inches above eye level.
(5) Sit at least 20 inches (or an arm length) away from the computer screen.
(6) Stand up and walk around a few minutes periodically.
(7) Do not use phone kept on shoulder while you sit on the chair. Alternatively you may use headsets for comfortable phone conversation without causing any strain on shoulders.
(8) Keep monitor clean and free from dust and greasy hand stains to prevent any strain on eyes while viewing displaying on the screen.
(9) Try to keep arm at right angle at most times while using keyboard and mouse in the front of the computer.
(10) Do not rest your palm on the keyboard while typing.
(11) Avoid eye fatigue by resting and refocusing your eyes periodically look away from the monitor and focus on something in distance.
Maintaining your Monitor
Do:
v Keep the brightness and contrast at minimum before switching on the system and increase it to the appropriate level thereafter.
Don’t:
v Try to open the VDU and touch the parts as these parts may carry high voltage.
Maintaining your keyboard
Do:
v Clean the keyboard regularly.
v Use a vacuum cleaner keyboards as it can extract the dust collected between the keys.
Don’t
v Strike the keys hard as those of a manual typewriter since these keys are soft touch.
v Rest your hands on the keyboard. Keep anything on your keyboard.
v Use the keys after switching off the system.
v Stretch the keyboard cable.
Social and Ethical Behavior
Accessing the personal information of others on the computer violates ethical principles. Computer Ethics is a set of moral principles that govern an individual or a group on ? what is acceptable behaviors while using a computer.
Some of the rules that the students should follow while using computers are the following:
1. Do not use the computer to harm other users.
2. Do not use computers to steal other’s information.
3. Do not access files without the permission of the owner.
4. Do not copy copyrighted software without the author’s permission.
Question 1:
कक्षा में साथियों के साथ बातचीत करो।
(क) तुम्हें कहानी में कौन सबसे अच्छा लगा? क्यों?
(ख) मक्खी मकड़ी के जाल में फँस गई थी। फिर क्या हुआ होगा? कहानी आगे बढ़ाओ।
Answer:
(क) हमें कहानी में सबसे अच्छी लोमड़ी लगी क्योंकि उसने बड़ी ही समझदारी से घमंडी मक्खी को मकड़ी के जाल में फंसाकर मार दिया और सबको बचा लिया।
(ख) मक्खी, मकड़ी को पकड़ने जब उसके जाल में घुसी तो वहाँ फंस गई। उसने जाल से निकलने की बहुत कोशिश की परन्तु जितनी कोशिश करती उतना ही फंसती जाती। इस तरह से उसका घमंड चूर-चूर हो गया और आखिर में वह मर गई।
(नोट: इन प्रश्नों के उत्तर स्वयं देने का प्रयास करें।)
Question 1:
अगर कहानी का नाम मक्खी को ध्यान में न रखकर लोमड़ी और शेर को ध्यान में रखकर लिखा जाता तो उसके क्या-क्या नाम हो सकते थे?
Answer:
यदि लोमड़ी को ध्यान में रखकर कहानी का नाम दिया जाता तो चतुर लोमड़ी, समझदार लोमड़ी आदि होता। यदि शेर को ध्यान में रखकर कहानी का नाम दिया जाता, तो मूर्ख शेर, आलसी शेर होता।
Question 2:
अब तुम कहानी के लिए एक और नया शीर्षक सोचो। यह शीर्षक कहानी के किसी पात्र पर नहीं होना चाहिए। (कहानी की किसी घटना के बारे में शीर्षक हो सकता है।)
Answer:
कहानी का अन्य शीर्षक घंमडी का सिर नीचा, जैसी करनी, वैसी भरनी हो सकता है।
Question 1:
मक्खी ने जब शेर को जगाया तो वह आग बबूला हो गया। तुम्हें जब कोई गहरी नींद से जगाता है तो तुम क्या करते हो?
Answer:
जब हमें कोई गहरी नींद से जगाता है, तो हम गुस्सा नहीं करते बल्कि उसे कहते हैं कि हमें सोने दो नींद आ रही है या अभी थोड़ी देर में उठते हैं।
Question 2:
मक्खी उड़ाते-उड़ाते शेर ऊब गया था। तुम क्या करते-करते ऊब जाते हो?
Answer:
1) हम खाली बैठे-बैठे ऊब जाते हैं। 2) कभी-कभी बहुत देर तक पढ़ते-पढ़ते ऊब जाते हैं। 3) कई बार बहुत देर तक खेलते-खेलते भी ऊब जाते हैं। 4) कभी हमारा दोस्त अपनी एक ही बात कई बार सुनाता है, तो भी ऊब जाते हैं।
Question 3:
मान लो तुम शेर हो। मक्खी ने तुम्हारे साथ जो कुछ भी किया वह लोमड़ी को बताओ।
Answer:
लोमड़ी बहन देखो इस मक्खी ने मुझे कितना तंग किया हुआ है। इसने मुझे पूरे दिन सोने नहीं दिया। मेरे मना करने पर और भी तंग कर रही है। जब मैंने मारने की धमकी दी, तो वह लड़ने को तैयार हो गई। वह कभी मेरे माथे, कभी हाथ, कभी नाक, कभी कान पर बैठ जाती है। अपने पंजे से उसे मारने की कोशिश करते-करते मैं खुद ही घायल हो गया हूँ। मैं उससे बड़ा परेशान हूँ। मुझे इससे बचाओ।
Page No 12:
Question 4:
शेर तो भोजन करके आराम कर रहा था। तुम खाना खा कर क्या करते हो?
• अक्सर ……………………………………………………………
• कभी-कभी ………………………………………………………..
Answer:
अक्सर स्कूल से आकर खाना खाकर आराम करते हैं।
कभी-कभी आराम करते हुए टेलीविज़न भी देखते हैं।
Question 5:
शेर ने भोजन में क्या खाया होगा? तुम क्या-क्या खाते हो?

Answer:

Question 1:
नीचे कहानी से जुड़ी तस्वीरें गई हैं। उसमें कुछ न कुछ बोला जा रहा है। सोचो और लिखो कौन क्या बोल रहा है?
 |  |
| …………………………………………….. | …………………………………………….. |
| …………………………………………….. | …………………………………………….. |
 |  |
| …………………………………………….. | …………………………………………….. |
| …………………………………………….. | …………………………………………….. |
 |
| …………………………………………….. |
| …………………………………………….. |
Answer:




Page No 13:
Question 1:
कहानी के हिसाब से बताओ।
| घमंडी | ……………………………….. |
| चतुर | ……………………………….. |
| समझदार | ……………………………….. |
| डरपोक | ……………………………….. |
| सबसे चतुर | ……………………………….. |
| आलसी | ……………………………….. |
Answer:
| घमंडी | मक्खी |
| चतुर | हाथी |
| समझदार | हाथी |
| डरपोक | शेर |
| सबसे चतुर | लोमड़ी |
| आलसी | हाथी |
Page No 14:
Question 1:
चुटकी बजाने का मतलब होता है ‘बहुत जल्दी कर लेना।’
(क) तुम कौन-कौन से काम चुटकी बजाते ही कर लेते हो? बताओ।
(ख) अब तुम अपनी एक टोली बनाओ। तुममें से एक लीडर बनेगा। वह बाकी बच्चों को करने के लिए काम देगा जिसे चुटकी बजाते ही करना होगा। जैसे– बाहर से पाँच पत्तियाँ लाओ और उनके नाम बताओ या शेखीबाज़ मक्खी के पात्रों के नाम बताओ। जो सबसे जल्दी कर ले वह लीडर बने।
Answer:
(क) मैं कंघा करना, जूते पहनना, दूध पीना, आइसक्रीम खाना आदि काम चूटकी बजाते ही पूरे कर लेता हूँ।
(ख) हमने गीता, सीता, मोहन, मनन, विमल को लेकर टोली बनाई इसमें पाँच जगहों के नाम, पाँच सींग वाले जानवरों के नाम, पाँच रस वाले फलों के नाम लिखने के लिए कहा। एक-एक पर्ची हर एक को दी गई। सबसे पहले मनन ने बताया उसे लीडर बना दिया गया।
(नोट: विद्यार्थियों को दूसरे प्रश्न को अपने सहपाठियों की सहायता से पूरा करना है।)
Question 1:
यह मकड़ी उस रास्ते से जाना चाहती है, जिस पर चलकर सबसे ज़्यादा जाले मिलें। अंदर जाने के लिए 1, 2, 3, 4 और 5 में से कौन-सा रास्ता होगा?
Answer:
चित्र में न. 4 वाला रास्ता ज़्यादा जाले वाला है। इसमें आठ जाल आते हैं।
(नोट: विद्यार्थी किताब में चित्र देखकर स्वयं करें।)
Page No 15:
Question 1:
इन वाक्यों को अपने ढंग से लिखकर बताओ।
(क) शेर आग-बबूला हो उठा।
(ख) उसकी ज़रा खबर लो न।
(ग) उस मकड़ी को तो मैं चुटकी बजाते ही खत्म कर देती हूँ।
(घ) जंगल के राजा के मुँह से ऐसी भाषा कहीं शोभा देती है!
Answer:
(क) शेर गुस्से से पागल हो गया।
(ख) उसके बारे में पता करो या उसे जा कर ठीक से समझाओ।
(ग) उस मकड़ी को शीघ्र ही मार देती हूँ।
(घ) जंगल के राजा को ऐसा नहीं कहना चाहिए।
Question 1:
इनके पास तुमने अक्सर किन-किन को उड़ते-मँडराते देखा है?
| (क) | जलते बल्ब के आसपास | …………………………… |
| (ख) | खेतों में | …………………………… |
| (ग) | इकट्ठे पानी के ऊपर | …………………………… |
| (घ) | फूलों पर | …………………………… |
| (ङ) | कचरे के ढेर पर | ……………………………. |
| (च) | हलवाई की मिठाइयों पर | ……………………………. |
Answer:
| (क) | जलते बल्ब के आसपास | मच्छर, छिपकली, पंतगे |
| (ख) | खेतों में | टिड्डियाँ, मच्छर, चिड़ियाँ |
| (ग) | इकट्ठे पानी के ऊपर | मच्छर, मक्खी |
| (घ) | फूलों पर | भंवरे, तितलियाँ, |
| (ङ) | कचरे के ढेर पर | मच्छर, मक्खियाँ |
| (च) | हलवाई की मिठाइयों पर | मक्खियाँ, मधुमक्खियाँ |
Question 1:
क्या तुम किसी शेखीबाज़ को जानते हो? कौन है वह? वह किस चीज़ के बारे में शेखी बघारता है?
Answer:
मेरी एक सहेली है जो अपनी हर चीज़ की शेखी बघारती है। वह अपनी हर चीज़ को कीमती व विदेशी बताती रहती है। अपने हर काम को बढ़ा-चढ़ा कर बताती है।
Story Construction
The process of step-wise arrangement of the ideas, acts and occurrences which gives us some moral or idea is called a story. The main parts of a story are:
(i) Heading
(ii) Plot
(iii) Moral
Some stories are given below:
Story – 1: Unity is Strength
A poor farmer had four sons. They did not help their father in the field. They always quarrelled among themselves. The farmer was unhappy. He tried to set them right, but in vain.
The farmer was always sad. He fell ill. His end was near. He wanted to unite his sons. He thought of a plan. He called his sons. He gave them a bundle of sticks. He asked them to break it. Each tried to break the bundle but failed.
The father then untied the bundle. The sons broke the sticks easily. At this the father said, “Be united like the bundle. If you are united none will harm you.” The sons learnt a lesson. They never quarrelled again.
Moral: United we stand, divided we fall.
Story – 2: The Hidden Treasure
There was an old farmer. He had four lazy sons. Before dying he wanted to teach his sons the value of hard work. He called his sons to his bed-side. He said, “Dear sons, long ago my father gave me a box full of gold coins. For fear of robbers, I buried it in the fields. I want you to dig it out after my death and lead a happy life.”
After a few days, the farmer passed away. The sons went to fields with spades and pick- axes. They dug every inch of the ground. But no treasure was found. A passerby asked them to sow wheat. The sons did so. They reaped a rich harvest that year. They realized that the real treasure was in hard work. This was what their father wanted to teach them.
Moral: Hard work is the real treasure.
Story – 3: Two Friends and the Bear
Mohan and Sohan were friends. They lived in a village. Mohan was true and loyal but Sohan was selfish.
One day they set out on a long journey their way lay through a thick forest. As they were passing through it, they saw a bear. It was coming towards them. Sohan at once climbed up a nearby tree. He was now safe. Mohan did not know how to climb a tree. But he did not lose his presence of mind. He had heard that the bear did not eat the dead.
So he lay down on the ground and held his breath.
The bear came. It sniffed Mohan and took him for a dead man. So it went away. Now Sohan got down the tree. He said to Mohan, “What did the bear say in your ear?” Mohan replied, “The bear advised me not to trust a false friend.” Sohan felt ashamed.
Moral: A friend in need is a friend indeed.
Story – 4: Good out of Evil
Once there lived a merchant in a village. One day he earned a lot of money and was returning home. His way lay through a thick forest. The forest was infested with robbers, so he was in a hurry. He had not gone very far when it began to rain. He was drenched to the skin. He grew angry and cursed God for the untimely rain and bad weather. As he was doing so, he came across a robber with a loaded pistol in his hand. Pointing the pistol towards the merchant, the robber said, “your life or your money!” The merchant did not lose heart and kept his presence of mind. He began to run as fast as he could. The robber gave him a hot chase.
Soon the robber overtook the merchant. He aimed at him with his pistol and pulled the trigger. The gunpowder had become wet due to heavy rain, so the pistol did not go off. The merchant escaped unhurt. Then he thanked God for rain and bad weather. He concluded that his safety was due to the rain and said, “Sometimes good comes out of evil.”
Moral: God does everything for our good.
Story – 5: The Farm Dog and the Wolf
Once there was a wolf. He came to a farm. He met the farm dog. The dog was quite healthy. The wolf was thin. The wolf asked him the secret of his health. The dog replied that he kept watch over the farm and his master fed him well. The dog advised him, “Do honest work, master will feed you well.” The wolf agreed.
The wolf noticed some marks round the dog’s neck. He asked the dog about it. The dog replied that during the day he had to wear the chain round his neck. The wolf was shocked to hear this. He said, “I would rather be free and starve than be a slave to anybody.”
Moral: Better be hungry than in chains.
Story – 6: The Hare and the Lion
A lion lived in a forest. He was the king of the animals. He killed many animals. The animals were in terror. They held a meeting. An old hare stood up. He was wise. He suggested a plan. All the animals went to the lion. The animals told him that they will send one animal every day. The lion agreed.
Everyday a new animal was sent to lion. The lion fed on the animal. One day it was a hare’s turn. He reached the lion late. The lion was angry. He asked him why he came late. The hare said that another lion had held him on the way. The lion told him to show the other lion. The hare led him to a deep well. The lion looked into the well and saw his own image in the water. He took his image for another lion. He at once jumped into the well and died. All the animals were happy.
Moral: Brain is mightier than brawn.
The story of Fire
- In the beginning, thousands of years ago man did not know how to control fire.
- When forest fires happened, man may have ate roasted food and liked it. Since then he started roasting roots and animal food.
- He kept on burning dried twigs since he did not know how to produce fire. Later, he came to know that fire can be produced by striking two stones.
- Fire is used to cook food and many other activities such as melting metals.
- Now we have kerosene stoves, matchsticks, wood, coal, petrol, LPG, etc., to produce fire. We use it as a means of energy.
- We should not play with fire. We should always turn off the LPG cylinder when not in use.
रिमझिम पाठ- 1. Class 3 Hindi Kakku
नाम ही नाम
प्रश्न 1. तुम अपना नाम लिखो और बताओ की तुम्हारे नाम का क्या मतलब है?
उत्तर- मेरा नाम आदित्य हैं| मेरे नाम का मतलब है- सूर्य|
तुम्हारे कितने नाम
प्रश्न- तुम्हे लोग और किन-किन नामों से बुलाते हैं?
उत्तर-
| प्यार वाला नाम | चिढाने वाला नाम | दोस्तों का दिया नाम |
| अमीछोटू | लम्बूतोंदू | अक्कूसोनू |
प्रश्न- सोचो और लिखो की किसी-किसी को नीचे दिए नामों से क्यों बुलाया जाता होगा?
उत्तर- गप्पू इधर-उधर की बातें करने वाला
भोली जो सीधी-सादी हो|
छुटकी जिसका कद छोटा हो|
गोलू जिसका चेहरा गोल मटोल हो|
प्रश्न- अब बताओ तुम्हारा कौन-सा दोस्त, कौन-सी सहेली
उत्तर- भक्कू है मान्नी, मोनू
झक्कू है विनीत, कांता
गप्पू है माला, अक्षित
अब कविता का समय
प्रश्न- कक्कू वह जो सदा हँसाए
उत्तर- रोना उसे ज़रा ने भाए
चिड़िया के संग गाना गाए
संग मोर के नाचे
इसीलिए तो कभी-कभी हम
कहते उसको कक्कू
कक्कू क्या है?
प्रश्न- कक्कू कोयल जैसा क्यों नहीं है? लिखो|
उत्तर- कक्कू दिनभर रोता है| उसकी आवाज़ भी मीठी नहीं है| उसे गाना बिलकुल नहीं आता, इसलिए वह कोयल जैसा नहीं है|
नामों की रेल
प्रश्न 1. पाँच-पाँच बच्चों की टोली बना लो| अब अपनी-अपनी टोलियों के बच्चों के नाम रेल के डिब्बों में लिखो|
उत्तर- मनोज, नीतू, हरीश, गौरव, अमित
प्रश्न 2. वर्णमाला याद है न? चलो, इन नामो को वर्णमाला क हिसाब से कर्म में लगाते हैं|
उत्तर- अमित गौरव नीतू मनोज हरीश
चिढ़ाना
प्रश्न- क्या तुम्हें भी कोई चिढ़ाता है? तब तुम्हें कैसा लगता है? कक्षा में चर्चा करो|
उत्तर- मुझे मेरे मित्र चिढाते हैं|
जब मुझे वह चिढाते हैं तो मुझे बहुत बुरा लगता है| उन पर क्रोध आता है| मन करता हसी कि सभी से झगड़ा करूँ| मैं उनकी ओर ज़रा भी दयां नहीं देता| मुझे यह बिलकुल पसंद नहीं लगता कि मुझे चढाए हमें किसी को चिढ़ाना नहीं चाहिए| इससे शत्रुता और भेदभाव बढ़ता है|
Maths
Introduction
Money is the medium of exchange. We pay the money equivalent to the cost of things we buy. It is available in two forms, coins and notes. In ancient word coins were made up of gold and silver.
Conversion of Money
Conversion of Rupees into Paise
Hundredth part of one rupee is one paise. Therefore, rupees and paise are converted into each other by the factor of 100.
Following are the steps used in the conversion of rupees into paise.
Step 1: To convert rupees into paise, multiply the number of rupees by 100.
Step 2: Resulting product is obtained in paise.
i. e. Rupees 5 = 5 × 100 paise= 500 paise.
Conversion of Paise into Rupees
Following are the steps used in the conversion of paise into rupees.
Step 1: Divide paise by 100.
Step 2: Put a dot mark after two digits from right in paise,
Step 3: The resulting product is obtained in rupees.
- Example
How much A will get if B gives 34 of 5 rupees coins?
(a) 16000 paise (b) 17000 paise
(c) 10000 paise (d) All the above
(e) None of these
Ans. (b)
Explanation: A will get ` 34 × 5 = ` 170 = 17000 paise.
Operations on Money
Addition of Money
Following are the steps used in the addition of money,
Step 1: Arrange the money vertically, rupees under rupees column and paise under paise column.
Step 2: Add the money from right or paise.
Step 3: If carry is generated then add the carry to the next addition.
Step 4: The resulting value of money is their addition.
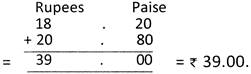
- Example
Add ` 18 and 20 paise and ` 20 and 80 paise.
Subtraction of Money
Following are the steps used in the subtraction of money.
Step 1: Arrange the money vertically, rupees under rupees column and paise under paise column.
Step 2: Subtract the money starting from right or paise.
Step 3: Take borrow if required.
- Example
Subtract ` 34.50 from ` 45.10
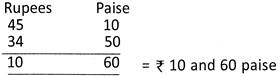
- Example
Money paid by Peter to a shopkeeper is ` 45 for the cost of rice and ` 75.50 for the cost of oil. How much money is paid by Peter?
(a) ` 100.50 (b) ` 121.45
(c) ` 120.50 (d) All the above
(e) None of these
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Money paid by peter = ` 45 + ` 75.00 = ` 120.50
Unitary Method
Unitary method is self-indicating, In other words, this is the method informing the cost of unit article, if the cost of more than one article is given. This method is widely used for the simplification of word based problems.
Use of Unitary Method for Solving Money Based Problems
The value of required number of articles is obtained by finding the value of unit article.
- Example
What is the cost of 1 article if the cost of 10 articles is ` 2500?
(a) ` 250 (b) ` 350
(c) ` 300 (d) ` 150
(e) None of these
Ans. (a)
Explanation: Cost of 1 article =totalcostNumberofarticles
Ø Example
Find the cost of one fourth of 56 apples if the cost of an apple is ` 7
(a) ` 88 (b) ` 98
(c) ` 78 (d) ` 68
(e) None of these
Ans. (b)
Explanation: Number of apples =564=14
Total cost = ` (14 × 7) = ` 98.










